What is Self-Concept Theory? A Psychologist Explains
 Who are you? What makes you “you?”
Who are you? What makes you “you?”
You might answer with “I’m a mother,” or, “I’m a therapist,” or maybe, “I’m a believer,” “I’m a good friend,” “I’m a brother.”
Maybe you answer with, “I am excellent at my job,” “I’m an accomplished musician,” or “I’m a successful athlete.”
Other responses might fall into the category of traits: “I’m a kind-hearted person,” “I’m intelligent and hard-working,” or “I’m laid-back and easy-going.”
These responses come from your internal sense of who you are. This sense is developed early in life, but it goes through constant evaluation and adjustment throughout the lifespan.
In psychology, this sense of self has a specific term: self-concept.
Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our three Self-Compassion Exercises for free. These detailed, science-based exercises will not only help you understand and show more compassion and kindness to yourself but will also give you the tools to help your clients, students or employees improve their self-compassion.
This Article Contains:
- What is Self-Concept? A Definition
- Self-Concept Theory
- The Components and Elements of the Self-Concept Model
- The Development Stages of Self-Concept
- 10 Examples of Self-Concept
- Research on Self-Concept
- Measuring Self-Concept with Scales, Tests, and Inventories
- Self-Concept Activities and Lesson Plans for Preschoolers and Older Students (PDF)
- Self-Concept Worksheets (PDF)
- 8 Quotes on Self-Concept
- A Take-Home Message
- References
What is Self-Concept? A Definition
Self-concept is an overarching idea we have about who we are—physically, emotionally, socially, spiritually, and in terms of any other aspects that make up who we are (Neill, 2005). We form and regulate our self-concept as we grow, based on the knowledge we have about ourselves. It is multidimensional, and can be broken down into these individual aspects.
For example, you may have a very different idea of who you are in terms of your physical body, and who you are in terms of your spirit or soul.
The influential self-efficacy researcher Roy Baumeister (1999) defines self-concept as follows:
“The individual’s belief about himself or herself, including the person’s attributes and who and what the self is.”
A similar definition comes from Rosenberg’s 1979 book on the topic; he says self-concept is:
“…the totality of an individual’s thoughts and feelings having reference to himself as an object.”
Self-concept is related to several other “self” constructs, such as self-esteem, self-image, self-efficacy, and self-awareness. In the following section, we will explain these slight—yet important—differences.
Self-Concept vs. Self-Esteem
Self-concept is not self-esteem, although self-esteem may be a part of self-concept. Self-concept is the perception that we have of ourselves, our answer when we ask ourselves the question “Who am I?”
It is knowing about one’s own tendencies, thoughts, preferences and habits, hobbies, skills, and areas of weakness. According to Carl Rogers, founder of client-centered therapy, self-concept is an overarching construct that self-esteem is one of the components of it (McLeod, 2008).
Self-Concept vs. Self-Image
Self-image is related to self-concept but is less broad. Self-image is how an individual sees themselves, and it does not have to align with reality.
A person’s self-image is based on how they see themselves, while self-concept is a more comprehensive evaluation of the self, largely based on how a person sees themselves, values themselves, thinks about themselves, and feels about themselves.
Carl Rogers posited that self-image is a component of self-concept, along with self-esteem or self-worth and one’s “ideal self” (McLeod, 2008).
Self-Concept vs. Self-Efficacy
Self-concept is a more complex construct than self-efficacy. While self-efficacy refers to an individual’s judgments of their own abilities, self-concept is more general and includes both cognitive (thoughts about) and affective (feelings about) judgments about oneself (Bong & Clark, 1999).
Self-Concept vs. Self-Awareness
Self-awareness also influences self-concept. It is the quality or trait that involves conscious awareness of one’s own thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and traits (Cherry, 2018A). To have a fully developed self-concept (and one that is based in reality), a person must have at least some level of self-awareness.
We explore this further in The Science of Self-Acceptance Masterclass©.
Self-Concept Theory

Generally, theorists agree on the following points:
- On the broadest level, self-concept is the overall idea we have about who we are and includes cognitive and affective judgments about ourselves;
- Self-concept is multi-dimensional, incorporating our views of ourselves in terms of several different aspects (e.g., social, religious, spiritual, physical, emotional);
- It is learned, not inherent;
- It is influenced by biological and environmental factors, but social interaction plays a big role as well;
- Self-concept develops through childhood and early adulthood when it is more easily changed or updated;
- It can be changed in later years, but it is more of an uphill battle since people have established ideas about who they are;
- Self-concept does not always align with reality. When it does, our self-concept is “congruent.” When it doesn’t, our self-concept is “incongruent.”
Identity and Self-Concept Theory in Psychology vs. Self-Concept in Sociology
Both psychology and sociology share an interest in self-concept, but they use slightly different ways to explore it. Individual researchers vary, of course, but generally, the divide can be thought of in these terms:
- Sociology/social psychology focuses on how self-concept develops, specifically within the context of the individual’s social environment.
- Psychology focuses on how self-concept impacts people (Gecas, 1982).
There are other differences between the two, including psychology’s general focus on the individual versus sociology’s focus on the group, community, or society; however, this difference in focus has led to two diverse research streams. Both have resulted in great insights and interesting findings, and they sometimes overlap, but this divide can still be seen in the literature today.
Carl Rogers and the Self-Concept Theory of Personality
Famed psychologist, theorist, and clinician Carl Rogers posited a theory of how self-concept influences and, indeed, acts as the framework for, one’s personality.
The image we have of who we are contributes to our personality, and our actions—combined with our personality —create a feedback loop into our image of ourselves. Rogers believed that our personality is driven by our desire for self-actualization. This is the condition that emerges when we reach our full potential and our self-concept, self-worth, and ideal self all overlap (Journal Psyche, n.d.).
How we develop our personalities and self-concepts varies, thus creating the unique individuals we are. According to Rogers, we always strive for self-actualization, some with more success than others.
How do people go about striving for self-actualization and congruence? This relates to the idea of how anyone “maintains” their idea of themselves. We explore that next.
Self-Concept Maintenance Theory
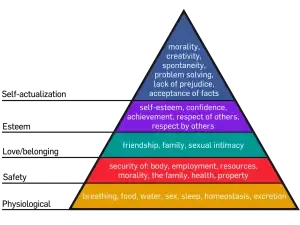
Self-concept maintenance refers to how people maintain or enhance their sense of self. It is relatively fixed after a person reaches adulthood, but it can—and does—change based on the person’s experiences.
The theory of self-concept maintenance states that we do not simply sit and wait for our self-concept to develop: we take an active role in shaping our self-concept at all ages (whether we are aware of this or not).
Although there are different theories about the processes of self-concept maintenance, it generally concerns:
- Our evaluations of ourselves
- Our comparison of our actual selves with our ideal selves
- Our actions taken to move closer to our ideal selves (Munoz, 2012).
This may seem like a pretty logical and straightforward process, but we tend to give ourselves room for moral ambiguity. For example, a study by Mazar, Amir, and Ariely (2007) showed that people will generally engage in beneficial dishonesty when given the opportunity. However, these same people might not revise their self-concept to incorporate this dishonesty.
When participants in the study were prompted to be more aware of their internal standards for honesty, they were less likely to engage in beneficial dishonesty; on the other hand, when given a “degrees of freedom” (greater separation between their actions and the rewards they would receive for dishonesty), they were more likely to engage in dishonesty—with no impact to their self-concept.
This is one example of the work on self-concept maintenance, as humans constantly assess themselves and their moral code since it influences their identity and actions.
Self-Concept Clarity and Self-Concept Differentiation
Self-concept clarity is different from self-concept.
Self-concept clarity (SCC) refers to how clear, confident, and consistent an individual’s definitions of themselves are (Diehl & Hay, 2011). Self-concept differentiation (SCD) refers to how an individual’s self-representation may vary across contexts or social roles (e.g., self as a spouse, self as a parent, self as a student).
SCC and SCD are hot topics in psychology since they influence thought patterns and behavior.
Higher SCC indicates a firmer and more stable self-concept, while low SCC indicates that an individual is unclear or vague about who they really are. Those with low SCC may struggle with low self-esteem, self-consciousness, and neuroticism.
SCD is not as clear-cut. Having a high SCD may be viewed as a bad thing, but it can also be an effective coping mechanism for succeeding in the modern world where individuals have many different roles. If SCD is very high, it might mean that the individual does not have a stable self-concept and “wears a different mask” for each of their roles.
A very low level of SCD may indicate that the individual is authentically “them” across all of their roles—although it may also indicate that he cannot effectively switch from one role to another (Diehl & Hay, 2011).
Essentially, people who differentiate their roles slightly, yet maintain a clear image of themselves, may succeed most at finding balance in their identity and image.
The Components and Elements of the Self-Concept Model
There are different ideas about what self-concept consists of, and how it should be defined; however, there are some characteristics and dimensions that apply to the basic, agreed-upon conceptualization of self-concept.
Characteristics of Self-Concept
As a brief review, self-concept is the perspective we have on who we are. Each of us has a unique self-concept, different from the self-concept of others and from their concept of us.
However, there are some characteristics that all of our self-concepts have in common.
Self-concept:
- Displays uniquely with each person.
- Vary from very positive to very negative.
- Carries emotional, intellectual, and functional dimensions.
- Changes with the context.
- Changes over time.
- Influence the individual’s life (Delmar Learning, n.d.)
Dimensions of Self-Concept
Different dimensions may constitute different kinds of self-concept; for example, the dimensions that create “academic self-efficacy” will not have as much overlap with “social self-efficacy.”
There are some overarching dimensions that researchers understand with the self-concept puzzle. These dimensions include:
- Self-esteem
- Self-worth
- Self-image (physical)
- Ideal self
- Identities or roles (social)
- Personal traits and qualities (Elliot, 1984; Gecas, 1982)
The Development Stages of Self-Concept

Early childhood is a ripe time for young humans to perceive themselves in the world.
The Formation of Self-Concept During Early Childhood
There are three general stages of self-concept development during early childhood:
- Stage 1: 0 to 2 years-old
a. Babies need consistent, loving relationships to develop a positive sense of self.
b. Babies form preferences that align with their innate sense of self.
c. Toddlers feel secure with gentle but firm limits
d. At age two, language skill develops and toddlers have a sense of “me.” - Stage 2: 3 to 4 years-old
a. Three and four-year-olds begin to see themselves as separate and unique individuals.
b. Their self-images tend to be descriptive rather than prescriptive or judgmental.
c. Preschoolers are increasingly independent and curious about what they can do. - Stage 3: 5 to 6 years-old
a. They are transitioning from the “me” stage to the “us” stage, where they are more aware of the needs and interests of the larger group.
b. Kindergarteners can use their words to communicate their wants, needs, and feelings.
c. Five and six-year-olds can use even more advanced language to help define themselves within the context of the group (Miller, Church, & Poole, n.d.).
Self-Concept in Middle Childhood
During middle childhood (about 7 to 11 years old), children are beginning to develop a sense of their social selves and figuring out how they fit in with everyone else. They reference social groups and make social comparisons more often, and begin to think about how others see them.
Other characteristics of their self-concept at this stage include:
- More balanced, less all-or-none descriptions
- Development of the ideal and real self
- Descriptions of the self by competencies instead of specific behaviors
- Development of a personal sense of self (Berk, 2004)
Culture begins to play a big role at this stage, but we’ll talk more about that later.
The Development of Self-Concept in Adolescence
Adolescence is where the development of one’s self-concept really explodes.
This is the stage in which individuals (about age 12-18) play with their sense of self, including a time when they experiment with their identity, compare themselves with others, and develop the basis of a self-concept that may stay with them the rest of their life.
During this period, adolescents are prone to greater self-consciousness and susceptibility to the influence of their peers and chemical changes happening in the brain (Sebastian, Burnett, & Blakemore, 2008).
They enjoy greater freedom and independence, engage in increasingly competitive activities, compare themselves with their peers, and can value (even over-value) the perspective of others (Manning, 2007).
In adolescence, there are two important factors that influence self-concept and self-worth:
- Success in areas in which the adolescent desires success
- Approval from significant people in the adolescent’s life (Manning, 2007).
When students have a healthy sense of self-worth and self-esteem, they contribute to a greater self-concept.
10 Examples of Self-Concept
You may have a good handle on what self-concept is but these examples can help explain it more.
Self-concepts are rarely all positive or all negative; someone may have both positive and some negative self-concepts in different domains (e.g., a husband who thinks of himself as a good father but sees his physical self as out-of-shape and unhealthy or a student who think so themselves as a great athlete who struggles academically).
Some examples of positive self-concepts include:
- A person sees herself as an intelligent person;
- A man perceives himself as an important member of his community;
- A woman sees herself as an excellent spouse and friend;
- A person thinks of himself as a nurturing and caring person;
- A person views herself as a hard-working and competent employee.
On the flip side, these people could have negative self-concepts like:
- A person sees herself as stupid and slow;
- A man perceives himself as expendable and a burden on his community;
- A woman sees herself as a terrible spouse and friend;
- A person thinks of himself as a cold and unapproachable person;
- A person views herself as a lazy and incompetent employee.
We all have many of these mini or domain-specific self-concepts that encompass our self-concept. Some may be more positive or negative than others, and each is an important piece of what makes us who we are.
Self concept, self identity and social identity – Khan Academy
Research on Self-Concept
Given the marked interest in this topic within sociology and psychology, there is quite a bit of research out there on the subject. Here are a few of the most interesting and impactful findings on self-concept.
Self-Concept in Marketing and How it Influences Consumer Behavior
It probably won’t shock you that the idea of self-concept has made its way into marketing—after all, brands and companies can profit from targeting certain desirable identities. In fact, it is the basis of fashion and consumerism.
Our self-concept influences our wants and needs, and can also shape our behavior. Whether it is true or not, we tend to believe that our purchases will help establish our identity. There is a reason why people buy certain clothing, cars, etc.
And this idea has a name: self-concept attachment.
Self-Concept Attachment
Self-concept attachment refers to the attachment we form to a product as it influences identity. For example, someone who loves their Patagonia jacket may also consider it as a status symbol that also represents their “outdoorsy” side.
Thus, this jacket has a strong self-concept attachment, in addition to its purpose of providing warmth.
Surprisingly, consumers become more attached to a brand when the brands match their “actual selves” rather than their ideal selves (Malär, Krohmer, Hoyer, & Nyffenegger, 2011). We tend to identify more with brands that “meet us where we are” rather than trying to connect with our higher, ideal selves.
Companies understand this and work to (1) get to know their target consumers better, and (2) mold their brand identity to match the self-concept of their consumers. The more they can get consumers to identify with their brand, the more they will buy that brand.
How Does Self-Concept Affect Interpersonal Communication?
Think about a cycle in which we develop, maintain, and revise our self-concept: we have an idea of who we are, and we act in accordance with that self-concept. Consequently, others form an idea about who we are, and they react in accordance with their idea of who we are, thus impacting our idea of who we are.
This feedback loop continues to shape us, and interpersonal communication plays a big role here.
Our self-concept drives our motivations, methods, and experiences with communicating with others. For example, if you see yourself as someone who is always right (or who must always be right), you may struggle in communicating with others when disagreements arise.
If that need is accompanied by an acceptance of aggression, you may use hostility, assertiveness, and argumentativeness to attack the self-concepts of the people you are debating instead of discussing their positions (Infante & Wigley, 1986).
Communication on social media is also a determinant and an outcome of an individual’s self-concept.
Sponcil and Gitimu (2012) suggested that, in general, the more friends an individual has on social networking sites, the more positively they feel about themselves as a whole. Conversely, the anxiety of social media and maintaining one’s image poses separate issues.
Self-Concept and Academic Achievement
Self-concept and academic achievement is also a positive feedback loop, as actions beget similar actions and identity to match.
In a longitudinal study, Marsh (1990) found that students with more positive academic self-concept achieved greater academic success the following year. Later studies confirmed the relationship between the two but indicated that achievement affects self-concept more than self-concept inherently influences achievement success (Muijs, 2011).
Research by Byrne (1986) offered instead that self-concept and academic self-concept can be considered two separate constructs; academic achievement may impact one’s overall self-concept, but it is most directly related to academic self-concept.
Self-Concept and Career Development
Self-concept develops throughout the lifespan and during any career.
According to researcher Donald Super, there are five life and career development stages:
- Growth (Ages 0 to 14)
- Exploration (Ages 15 to 24)
- Establishment (Age 25 to 44)
- Maintenance (Age 45 to 64)
- Decline (Age 65+)
The first stage is marked by the development of one’s basic self-concept. In the second stage, able individuals experiment and try out new classes, experiences, and jobs. Stage 3 sees individuals establishing their career and building their skills, likely starting in an entry-level position.
In the fourth stage, individuals engage in a continuous management and adjustment process to both their self-concept and their career. Finally, the fifth stage is characterized by reduced output and preparations for retirement, activities which can have a huge impact on one’s self-concept (Super, Starishevsky, Matlin, & Jordaan, 1963).
Of course, this model assumes equal access and privilege upon entering the workforce, which is not truthful to reality. Not all humans, for example, have the opportunity to explore and establish themselves as easily as others.
Nevertheless, Super posited that self-concept drives career development and can act as a general framework and inspiration for future research in this area, including a social and racial unearthing of Rogers’ theory on self-actualization.
The research could also be conducted on Bandura’s work on self-efficacy, on role salience, and on the idea of multiple identities in career development (Betz, 1994).
Culture and Self-Concept
Unsurprisingly, culture can have a big impact on self-concept. For example, how children are treated in early childhood influences how their sense of self develops.
Many parents might be more concerned with emotions and satisfying the wants of their children, while others may be more firm and controlling of their child’s behavior, worrying about their needs rather than fulfilling their desires. This is a generalization, but one that holds under scrutiny: culture influence self-concept.
Research suggests that those from more collectivist cultures produced more group self-descriptions and fewer idiocentric self-descriptions than those from individualistic cultures (Bochner, 1994).
Further research also indicated that East Asian cultures are more accepting of contradictory beliefs about the self; this indicates that one’s self-concept in these cultures may be more flexible than, say, American culture (Choi & Choi, 2002).
Findings like these are fascinating, but they also reveal how and why it is difficult to measure self-concept. The next section summarizes those attempts.
Measuring Self-Concept with Scales, Tests, and Inventories

One’s self-concept does not always align with “reality” or with how others view a person. However, there are still some tools that can measure self-concept.
If you are interested in using a self-concept measure for research purposes, look first at the development of the instrument, the definition it is based on, and the dimensions or components it measures. It’s important that you choose a tool that aligns with the idea of self-concept that your research uses.
Some of the most prominent tools to measure self-concept include:
- The Robson Self-Concept Questionnaire (SCQ; Robson, 1989)
- The Social Self-Concept Questionnaire (SSC; Fernández-Zabala, Rodríguez-Fernández, & Goñi, 2016)
- The Academic Self-Concept Questionnaire (ASCQ; Liu & Wang, 2005)
Self-Concept Questionnaire by Dr. Saraswat
The Self-Concept Questionnaire from Dr. Saraswat (1984) has become a popular choice for measuring self-concept. It consists of 48 items measuring self-concept across six dimensions:
- Physical;
- Social;
- Temperamental;
- Educational;
- Moral;
- Intellectual.
For each item, the respondent rates how well each item describes their ideas about themselves on a 5-point scale. Higher scores indicate high self-concept, while low scores indicate low self-concept.
This self-concept questionnaire is generally thought of as reliable by researchers, but it is dated.
Self-Concept Activities and Lesson Plans for Preschoolers and Older Students (PDF)
If you’re looking for a great resource with 10 simple but effective activities for cultivating self-concept in young children, Glori Chaika’s article “Ten Activities to Improve Students’ Self-Concepts” can be adapted to fit the context for several age ranges.
We summarize the 10 activities she suggests here:
1 – The Interview
This activity is great for the beginning of the year as students to get to know their peers.
Break the group into pairs, and make sure each student is paired with someone they don’t very well. Give them 10 minutes to interview each other (5 minutes per interview) with fun questions like “would you rather live on a boat or on an island?” or “what is your favorite subject at this school?”.
When all of the interviews have been completed, have each pair come to the front of the class and introduce their partner to the other children.
2 – The Journal
Journals can be beneficial in many ways, as keeping a journal allows you to self-examine. Help your students develop their sense of self by assigning journal entries that they keep in one notebook all year.
Tell your students that they can put whatever they want in their journal—they can write a poem, describe a dream they had, write about what they hope for, something they are happy about, something they are sad about, etc.—and that they must make at least three entries (or however many you decide is appropriate) per week.
Make sure to tell them that you will only read the entry if they give you permission, but that you will check to ensure they have at least three dated entries per week.
3 – Designing Self-Collages
Self-collages are a great activity from young children to high-schoolers. Tell the students they need to create a collage that represents who they are by using pictures, words, and/or symbols. They can cut things from magazines, print them out from the internet, or draw pictures themselves.
You may want to guide them by suggesting to focus on things they enjoy or are good at, places they’ve been or would like to go, and people they admire.
When everyone’s collage is complete, you can do an extra activity where students present their collage to the classroom, or maybe everyone tries to guess which collage belongs to which student.
4 – Ranking Traits
This activity is best for older students with writing skills. Have the students rip a piece of paper into ten strips and write a word or phrase on each strip that they feel describes them. Tell them that no one will see the things they write down, so they can be completely honest.
Once the students have written down their ten traits, have them arrange them in order from those they most like about themselves to those they least like about themselves.
Encourage them to reflect on their traits by asking questions like:
- Do you like what you see?
- Do you want to keep it?
- Now give up one trait. How does the lack of that affect you?
- Now give up another. Give up three. Now what kind of person are you?
After the students have reduced their traits to six, have them add the traits back, one by one. For an extra boost to this activity, you can have the students journal about their experience at the end, and how they want to use their strengths.
5 – Accentuate the Positive
Accentuating the positive is all about noticing and sharing the positive things about others (and themselves).
To try this activity, break the students up into groups of four to six. Instruct the groups to pick one person (to start with) and tell that person all the positive things about them. Encourage the students to focus on traits and skills that can be altered (e.g., work ethic, skill in soccer), rather than permanent features (e.g., eyes, skin).
One student in each group will act as a recorder, writing down all the positive things that are said about someone. Each member of the group takes a turn, and the recorder gives the individual the list of all the positive things said about them at the end of the activity.
This exercise can also make a great focus for a journal entry.
6 – Thumbprints
This activity requires an ink pad and the willingness to get a bit messy!
Have each of your students place his or her thumb on the inkpad and then on a piece of paper to get a thumbprint. Show them the five major fingerprint patterns and have them identify their print type. Explain how fingerprints are unique—both across their own fingers and from person to person.
Next, have each student create an animal out of their thumbprint. Bonus points if the animal is one the student feels represents him or her! Encourage them to write about this in their journal, or to add the thumbprint drawing to their journal.
7 – Create a “Me” Commercial
This activity can be especially fun for the drama-loving students. Tell them that they are each going to make a two or three-minute commercial on why you should hire them.
The commercial should focus on their special skills, talents, and positive qualities. It should highlight what is great about them and what they would bring to the fictional position they are auditioning for.
Give the students some time to write their commercial, then have them present their commercials to the class. An alternative method for this activity is to have small groups create commercials for each group member.
8 – Shared Learning
This is a simple activity if you’ve been having your students write in their journal for the whole term.
Tell the students to look through their journal entries and reflect. Have them choose one thing they have learned about themselves during this term.
When each student has chosen something they would like to share, sit in a circle and have each student share out on what they learned over the past three months (or four months, or six months, etc.).
9 – Write Yourself a Letter
This is another activity that is appropriate for older children since it requires somewhat advanced writing skills.
Tell the students that they will be writing a letter to themselves, and to be totally honest since no one else will be able to read it. They can write whatever they’d like in this letter to their future selves, but they may want to add in things that describe them today (e.g., height and weight, current friends, favorite music and movies, special things that happened to them this year).
On another piece of paper or on the back of this letter, tell students to write down ten goals they would like to accomplish by this time next year. Have your students seal the letter and their goals in an envelope, address the envelope to themselves, and give it to you. In one year, mail the letters out to the students.
This is a far-reaching activity that will encourage your students to think about how they change over time, and how they stay the same.
10 – Drawing Self Portraits
Make sure that each student has access to a mirror for this activity. If there isn’t one handy in your classroom, bring some small mirrors in for the students to use.
Tell your students to use the mirror to draw a picture of themselves. It doesn’t have to look exactly like them, but it should be a good representation of them. This simple activity can promote self-reflection in students (beyond the kind that involves a mirror).
To take this activity a bit further, have them divide the drawing in half—on the left side, each student should draw herself as she sees herself, and on the right side, she should draw herself as she thinks others see her. Along with this drawing, the students can make an entry in their journal on the differences between how they see themselves and how they think others see them.
Self-Concept Activities for Preschoolers

For example, a few of the activities that can help preschoolers develop a self-concept include:
- Record each child’s voice during an activity period. Have the children listen to the voices and guess which voice goes with each child.
- Have several children stand in a line in front of the class. Name the child who is first, second, third and so on. Ask the children to change positions. Then have each child in line name his or her new position. To vary the activity, have the children at their seats name each child in line and describe his or her position.
- Make a friendship quilt. Cut several squares of brightly colored construction paper. Give each child one of the squares. Have them decorate the square or even glue a picture of himself, glitter, beads, sequins, or yarn to the square. Staple the squares, side by side, to the bulletin board. If extra squares are needed to fill in empty spaces, print the school’s name or teacher’s name on additional squares and intermingle them with the student’s squares.
- Have the children think of some things they can’t do now, but can do when they grow older. What are some things they can do now that they couldn’t do when they were younger?
- Role-play the growth process from baby to father or mother to grandparent. The child can interpret the process as he or she goes along. Children can also develop a short play about the family.
Any of these activities can be adapted to fit your children’s context, whether that is a classroom, at home, in a playgroup, in a therapy session, etc.
Lesson Plan on Self-Concept
If you’re looking for a good lesson plan on teaching self-concept, this plan from the Utah Education Network is a great choice.
It starts with a description of self-concept as “the person I think I am” and contrasts it with “the person others think I am” and “the person others think I think I am.”
A diagram on the first page shows a cycle with four “stops:”
- As I see myself
- My actions
- As others see me
- Other’s reactions to me
This diagram shows how each stop on the cycle feeds into the next, influencing each aspect and eventually coming back to the original stop. For example, how we see ourselves influences our actions. Our actions drive how others see us, and their image of us drives their reactions or behavior toward us.
Feedback on ourselves contributes to our overall image of ourselves, and the cycle continues.
Next, it describes several case studies to help drive the point home. There is the case of a 45-year old father who looks in the mirror and thinks about the wrinkle he just found, the weight he would like to lose, his desire to be a stay-at-home dad, his messy and unorganized house, and a commitment he made that has overextended him.
There is also a case of a middle-aged mother thinking about her miserable day at work, the last decade or so of overtime, her struggles to pay the bills and have a little money left for herself, and all the things she has on her to-do list.
A third case focuses on a teenage girl who is concerned about her skin, her haircut, whether her friends truly care about her, and an upcoming chemistry test that she has not studied for.
The final case concerns a teenage guy who was struggling to understand calculus and thinking back to the counselor that encouraged him to take it. He is also comparing himself to his straight-A brother and thinking about how he wished he could be the athlete his father wanted him to be. He is worrying about tryouts and doubting his ability to even make the team.
For each of these cases, the questions are:
- How will the individual see himself or herself?
- How will the individual act toward others?
- How will the individual think others see him or her?
- How will others act toward the individual?
- What effect does this have on how the individual sees him- or herself?
- Where is the spiral headed and how can its motion be reversed?
This is a great lesson for children to learn, whether you introduce it in elementary school (with some extra time and patience set aside!) or in high school.
Follow this link and click on “Self Concept Transparency” to see the example lesson plan for yourself, and feel free to invent examples most relevant to your class or client.
Self-Concept Worksheets (PDF)

Three of the most useful worksheets on self-concept are described below.
All About Me
This worksheet from the Utah Education Network is a good option for children of all ages.
It is only one page with 15 prompts to complete. These prompts are:
- I feel good about…
- I feel successful when…
- My favorite person is…
- My favorite activity is…
- I wish I could…
- I want to…
- If I could have three wishes, they would be:
a.
b.
c. - I feel depressed when…
- A character trait I need to improve is…
- I am good at…
- I wish I did not…
- My family is…
- I would like to be…
- The most important thing to me is…
- The thing I like best about myself…
You can find this worksheet and other worksheets and lesson plans on the Utah Education Network’s website here.
8 Quotes on Self-Concept
Learning about how others perceive a construct can be helpful in furthering our own understanding of that construct.
Use the quotes below to see how your idea of self-concept compares to the ideas of others.
What others think of us would of little moment did it not, when known, so deeply tinge what we think of ourselves.
Paul Valéry
Know, first, who you are; and then adorn yourself accordingly.
Epictetus
Seek out that particular mental attribute which makes you feel most deeply and vitally alive, along with which comes the inner voice which says, ‘This is the real me’, and when you have found that attitude, follow it.
William James
Today you are You, that is truer than true. There is no one alive who is Youer than You.
Dr. Seuss
Act as if you are the person you want to be.
Bernie Siegel
The self is not something that one finds. It is something that one creates.
Thomas Szasz
There is but one cause of human failure. And that is man’s lack of faith in his true Self.
William James
An individual’s self-concept is the core of his personality. It affects every aspect of human behavior: the ability to learn, the capacity to grow and change. A strong, positive self-image is the best possible preparation for success in life.
Joyce Brothers
A Take-Home Message
In this piece, we learned about what self-concept is (an overarching idea about who we are), how it comes about (it develops throughout the lifespan, and is most flexible in the early years), what it is related to and affected by (just about everything, but namely consumer behavior, academic achievement, career development, and culture), and whether you can do anything to change it—you can.
Our self-concept is affected by how we feel about ourselves and how we judge our abilities, competencies, and worth as a person. When we put some effort into boosting these self-evaluations, our self-concept will adjust to accommodate these changes.
We have the ability to change how we think about ourselves by working to become more like our ideal selves.
It might seem daunting to put in the effort required to revise your self-esteem and self-image, but like most tasks, getting started is the hardest part. Refer to some of the quotes above to get a dose of inspiration, or find some quotes on the subject that inspire you and keep them nearby whenever you’re in need of some motivation.
What do you think about self-concept? Do you have any other good quotes about self-concept? Do you have a developed self-concept or is it vaguer? Do you think it’s good or bad to have self-concept differentiation?
Let us know in the comments, and thanks for reading.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Self Compassion Exercises for free.
- Baumeister, R. F. (1999). The nature and structure of the self: An overview. In R. Baumeister (Ed.), The self in social psychology (pp. 1-20). Philadelphia, PA: Psychology Press (Taylor & Francis).
- Berk L. E. (2004). Development through the lifespan. Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
- Betz, N. E. (1994). Self-concept theory in career development and counseling. Career Development Quarterly, 43, 32-43.
- Bochner, S. (1994). Cross-cultural differences in the self concept: A test of Hofstede’s individualism/collectivism distinction. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 25, 273-283.
- Bong, M., & Clark, R. E. (1999). Comparison between self-concept and self-efficacy in academic motivation research. Educational Psychologist, 34, 139-153.
- Byrne, B. M. (1986). Self-concept/academic achievement relations: An investigation of dimensionality, stability, and causality. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science, 18, 173-186.
- Chaika, G. (2012). Ten activities to improve students’ self-concepts. Education World. Retrieved from http://www.educationworld.com/a_lesson/lesson/lesson085.shtml
- Cherry, K. (2018A). What is self-awareness? Very Well Mind. Retrieved from https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-self-awareness-2795023
- Cherry, K. (2018B). What is self-concept and how does it form? Very Well Mind. Retrieved from https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-self-concept-2795865
- Choi, I., & Choi, Y. (2002). Culture and self-concept flexibility. Personality and Social Psychology, 28, 1508-1517.
- Delmar Learning. (n.d.). Summary chapter 43: Self-concept. Nursing Fundamentals: Caring & Clinical Decision Making Online Companion. Retrieved from http://www.delmarlearning.com/companions/content/0766838366/students/ch43/summary.asp
- Diehl, M., & Hay, E. L. (2011). Self-concept differentiation and self-concept clarity across adulthood: Associations with age and psychological well-being. International Journal of Aging and Human Development, 73(2), 125-152.
- Elliot, G. C. (1984). Dimensions of the self-concept: A source of further distinctions in the nature of self-consciousness. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 13, 285-307.
- Fernández-Zabala, A., Rodríguez-Fernández, A., & Goñi, A. (2016). The structure of the Social Self-Concept (SSC) Questionnaire. Anales de Psicologia, 32, 199-205.
- Gecas, V. (1982). The self-concept. Annual Review of Sociology, 8, 1-33.
- Infante, D. A., & Wigley, C. J. (1986). Verbal aggressiveness: An interpersonal model and measure. Communication Monographs, 53, 61-69.
- Journal Psyche. (n.d.). Revisiting Car Rogers’ theory of personality. Retrieved from http://journalpsyche.org/revisiting-carl-rogers-theory-of-personality/
- Liu, W. C., & Wang, C. K. J. (2005). Academic self-concept: A cross-sectional study of grade and gender differences in a Singapore Secondary School. Asia Pacific Education Review, 6, 20-27.
- Malär, L., Krohmer, H., Hoyer, W. D., & Nyffenegger, B. (2011). Emotional brand attachment and brand personality: The relative importance of the actual and the ideal self. Journal of Marketing, 75, 35-52.
- Manning, M. A. (2007, February). Self-concept and self-esteem in adolescents. Principle Leadership Magazine, February 2007, 11-15.
- Marsh, H. W. (1990). Causal ordering of academic self-concept and academic achievement: A multiwave, longitudinal panel analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 646-656.
- Mazar, N., Amir, O., & Ariely, D. (2007). Mostly honest: A theory of self-concept maintenance. Unpublished Manuscript, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- McLeod, S. (2008). Self concept. Simply Psychology. Retrieved from https://www.simplypsychology.org/self-concept.html
- Miller, S. A., Church, E. B., & Poole, C. (n.d.). Ages & stages: How children develop self-concept. Scholastic. Retrieved from https://www.scholastic.com/teachers/articles/teaching-content/ages-stages-how-children-develop-self-concept/
- Muijs, R. D. (2011). Predictors of academic achievement and academic self-concept: A longitudinal perspective. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 67, 263-277.
- Munoz, L. (2012). Theories of self-concept maintenance. Life Long Learning: Social Psychology. Retrieved from https://lynnmunoz.wordpress.com/2012/11/22/theories-of-self-concept-maintenance/
- Neill, J. (2005). Definitions of various self constructs: Self-esteem, self-efficacy, self-confidence & self-concept. Wilderdom. Retrieved from http://www.wilderdom.com/self/
- Robson (1989). Development of a new self-report questionnaire to measure self-esteem. Psychological Medicine, 19, 513-518.
- Rosenberg, M. (1979). Conceiving the Self. New York, NY: Basic.
- Saraswat, R. K. (1984). Manual for Self-Concept Questionnaire. Agra, India: National Psychological Corporation.
- Sebastian, C., Burnett, S., & Blakemore, S. J. (2008). Development of the self-concept during adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Science, 12, 441-446.
- Sponcil, M., & Gitimu, P. (2012). Use of social media by college students: Relationship to communication and self-concept. Journal of Technology Research, 4.
- Super, D. E., Starishevsky, R., Matlin, N., & Jordaan, J. P. (1963). Career development; Self-concept theory. New York, NY: College Entrance Examination Board.
Let us know your thoughts
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (42)
- Coaching & Application (54)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (50)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (25)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (43)
- Optimism & Mindset (32)
- Positive CBT (25)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (45)
- Positive Emotions (30)
- Positive Leadership (14)
- Positive Psychology (32)
- Positive Workplace (33)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (42)
- Resilience & Coping (34)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (36)
- Software & Apps (13)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (44)
- Therapy Exercises (35)
- Types of Therapy (58)






What our readers think
If you don”t mind proceed with this extraordinary work and I anticipate a greater amount of your magnificent blog entries.
A stupendous offering indeed. Ackerman, the author, presents a comprehensive account of Self-Concept with stunning clarity and richness.
A sumptuously edifying gift for students of sociology and psychology everywhere.
Thank you so much. This helped a lot in my psychology project
Appreciating the persistence you put into your blog and detailed information you provide. I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.