Sending Homework to Clients in Therapy: The Easy Way
 Homework is an essential part of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT; Beck, 2011; Mausbach, Moore, Roesch, Cardenas, & Patterson, 2010).
Homework is an essential part of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT; Beck, 2011; Mausbach, Moore, Roesch, Cardenas, & Patterson, 2010).
Successful therapy relies on using assignments outside of sessions to reinforce learning and practice newly acquired skills in real-world settings (Mausbach et al., 2010).
Up to 50% of clients don’t adhere to homework compliance, often leading to failure in CBT and other therapies (Tang & Kreindler, 2017).
In this article, we explore how to use technology to create homework, send it out, and track its completion to ensure compliance.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free. These science-based exercises will explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.
This Article Contains:
Is Homework in Therapy Important?
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy has “been shown to be as effective as medications in the treatment of a number of psychiatric illnesses” (Tang & Kreindler, 2017, p. 1).
Homework is a vital component of CBT, typically involving completing a structured and focused activity between sessions.
Practicing what was learned in therapy helps clients deal with specific symptoms and learn how to generalize them in real-life settings (Mausbach et al., 2010).
CBT practitioners use homework to help their clients, and it might include symptom logs, self-reflective journals, and specific tools for working on obsessions and compulsions. Such tasks, performed outside therapy sessions, can be divided into three types (Tang & Kreindler, 2017):
- Psychoeducation
Reading materials are incredibly important early on in therapy to educate clients regarding their symptoms, possible causes, and potential treatments. - Self-assessment
Monitoring their moods and completing thought records can help clients recognize associations between their feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. - Modality specific
Therapists may assign homework that is specific and appropriate to the problem the client is presenting. For example, a practitioner may use images of spiders for someone with arachnophobia.
Therapists strategically create homework to lessen patients’ psychopathology and encourage clients to practice skills learned during therapy sessions, but non-adherence (between 20% and 50%) remains one of the most cited reasons for CBT failure (Tang & Kreindler, 2017).
Reasons why clients might fail to complete homework include (Tang & Kreindler, 2017):
Internal factors
- Lack of motivation to change what is happening when experiencing negative feelings
- Being unable to identify automatic thoughts
- Failing to see the importance or relevance of homework
- Impatience and the wish to see immediate results
External factors
- Effort required to complete pen-and-paper exercises
- Inconvenience and amount of time to complete
- Failing to understand the purpose of the homework, possibly due to lack of or weak instruction
- Difficulties encountered during completion
Homework compliance is associated with short-term and long-term improvement of many disorders and unhealthy behaviors, including anxiety, depression, pathological behaviors, smoking, and drug dependence (Tang & Kreindler, 2017).
Greater homework adherence increases the likelihood of beneficial therapy outcomes (Mausbach et al., 2010).
With that in mind, therapy must find ways to encourage the completion of tasks set for the client. Technology may provide the answer.
The increased availability of internet-connected devices, improved software, and widespread internet access enable portable, practical tools to enhance homework compliance (Tang & Kreindler, 2017).
How to Send Homework to Clients Easily

Clients who complete their homework assignments progress better than those who don’t (Beck, 2011).
Having an ideal platform for therapy makes it easy to send and track clients’ progress through assignments. It must be “user-friendly, accessible, reliable and secure from the perspective of both coach and client” (Ribbers & Waringa, 2015, p. 103).
In dedicated online therapy and coaching software, homework management is straightforward. The therapist creates the homework then forwards it to the client. They receive a notification and complete the work when it suits them. All this is achieved in one system, asynchronously; neither party needs to be online at the same time.
For example, in Quenza, the therapist can create a worksheet or tailor an existing one from the library as an activity that asks the client to reflect on the progress they have made or work they have completed.
The activity can either be given directly to the client or group, or included in a pathway containing other activities.
Here is an example of the activity parameters that Quenza makes possible.
The therapist selects the recipient, chooses when to send it, whether there will be a follow-up reminder, and who can see the completed worksheet.
A message can be attached to the activity, using either a template or a personally tailored message for the client. Here’s an example.
While sending out individual, targeted activities is highly effective, bundling them up into pathways for sharing at pre-arranged intervals may be even more helpful.
Once the activity is published and sent, the client receives a notification about a received assignment via their coaching app (mobile or desktop) or email.
The client can then open the Quenza software and find the new homework under their ‘To Do’ list.
Once the assignment is complete, the therapist receives a notification that it is ready for review.
Homework in Quenza: 5 Examples of Assignments
Quenza provides the ability to create your own assignments as well as a wide selection of existing ones that can be assigned to clients for completion as homework.
The following activities can be tailored to meet specific needs or used as-is. Therapists can share them with the client individually or packaged into dedicated pathways.
Such flexibility allows therapists to meet the specific needs of the client using a series of dedicated and trackable homework.
Examples of Quenza’s ready-to-use science-based activities include the following:
Wheel of Life
The Wheel of Life is a valuable tool for identifying and reflecting on a client’s satisfaction with life.
You can find the worksheet in the Positive Psychology Toolkit©, and it is also included in the Quenza library. The client scores themselves between 1 and 10 on specific life domains (the therapist can tailor the domains), including relationships, career development, and leisure time.
This is an active exercise to engage the client early on in therapy to reflect on their current and potential life. What is it like now? How could it look?
The wheel identifies where there are differences between perceived balance and reality.
The deep insights it provides can provide valuable input and prioritization for goal setting.
The Private Garden: A Visualization for Stress Reduction
While stress is a normal part of life, it can become debilitating and interfere with our everyday lives, stopping us from reaching our life goals.
We may notice stress as worry, anxiety, and tension and resort to avoidant or harmful behaviors (e.g., abusing alcohol, smoking, comfort eating) to manage these feelings.
Visualization is simple but a powerful method for reducing physical and mental stress, especially when accompanied by breathing exercises.
The audio included within this assignment helps the listener visualize a place of safety and peace and provides a temporary respite from stressful situations.
20 Guidelines for Developing a Growth Mindset
Research into neuroplasticity has confirmed the ability of the adult brain to continue to change in adulthood and the corresponding capacity for people to develop and transform their mindsets (Dweck, 2017).
The 20 guidelines (included in our Toolkit and part of the Quenza library) and accompanying video explain our ability to change mentally and develop a growth mindset that includes accepting imperfection, leaning into challenges, continuing to learn, and seeing ‘failure’ as an opportunity for growth.
Adopting a growth mindset can help clients understand that our abilities and understanding are not fixed; we can develop them in ways we want with time and effort.
Self-Contract
Committing to change is accepted as an effective way to promote behavioral change – in health and beyond. When a client makes a contract with themselves, they explicitly state their intention to deliver on plans and short- and long-term goals.
Completing and signing such a self-contract (included in our Toolkit and part of the Quenza library) online can help people act on their commitment through recognizing and living by their values.
Not only that, the contract between the client and themselves can be motivational, building momentum and self-efficacy.
The contract can be automatically personalized to include the client’s name but also manually reworded as appropriate.
The client completes the form by restating their name and committing to a defined goal by a particular date, along with their reasons for doing so.
Realizing Long-Lasting Change by Setting Process Goals
We can help clients realize their goals by building supportive habits. Process goals – for example, eating healthily and exercising – require ongoing actions to be performed regularly.
Process goals (unlike end-state goals, such as saving up for a vacation) require long-lasting and continuous change that involves monitoring standards.
This tool (included in our Toolkit and part of the Quenza library) can help clients identify positive actions (rather than things to avoid) that they must carry out repeatedly to realize change.
5 Counseling Homework Ideas and Worksheets
We have many activities that can be used to help clients attending therapy for a wide variety of issues.
In this section, we consider homework ideas that can be used in couples therapy, family therapy, and supporting clients with depression and anxiety.
Couples therapy homework
Conflict is inevitable in most long-term relationships. Everyone has their idiosyncrasies and individual set of needs. The Marital Conflicts worksheet captures a list of situations in which conflicts arise, when they happen, and how clients feel when they are (un)resolved.
Family therapy homework
Families, like individuals, are susceptible to times of stress and disruptions because of life changes such as illness, caring for others, and job and financial insecurity.
Mind the Gap is a family therapy worksheet where a family makes decisions together to align with goals they aspire to. Mind the gap is a short exercise to align with values and improve engagement.
How holistic therapist Jelisa Glanton uses Quenza
Homework ideas for depression and anxiety: 3 Exercises
The following exercises are all valuable for helping clients with the effects of anxiety and depression.
Activity Schedule is a template assisting a client with scheduling and managing normal daily activities, especially important for those battling with depression.
Activity Menu is a related worksheet, allowing someone with depression to select from a range of normal activities and ideas, and add these to a schedule as goals for improvement.
The Pleasurable Activity Journal focus on activities the client used to find enjoyable. Feelings regarding these activities are journaled, to track recovery progress.
Practicing mindfulness is helpful for those experiencing depression (Shapiro, 2020). A regular gratitude practice can develop new neural pathways and create a more grateful, mindful disposition (Shapiro, 2020).
Using Care Pathways & Quenza’s Pathway Builder
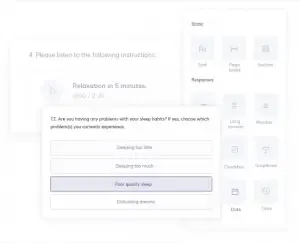
Each activity can be tailored to the client’s needs; shared as standalone exercises, worksheets, or questionnaires; or included within a care pathway.
A pathway is an automated and scheduled series of activities that can take the client through several stages of growth, including psychoeducation, assessment, and action to produce a behavioral change in a single journey.
How to build pathways
The creator can add two pathway titles. The second title is not necessary, but if entered, it is seen by the client in place of the first.
Once named, a series of steps can be created and reordered at any time, each containing an activity. Activities can be built from scratch, modified from existing ones in the library, or inserted as-is.
New activities can be created and used solely in this pathway or made available for others. They can contain various features, including long- and short-answer boxes, text boxes, multiple choice boxes, pictures, diagrams, and audio and video files.
Quenza can automatically deliver each step or activity in the pathway to the client following the previous one or after a certain number of days. Such timing is beneficial when the client needs to reflect on something before completing the next step.
Practitioners can also designate steps as required or optional before the client continues to the next one.
Practitioners can also add helpful notes not visible to the client. These comments can contain practical reminders of future changes or references to associated literature that the client does not need to see.
It is also possible to choose who can see client responses: the client and you, the client only, or the client decides.
Tags help categorize the pathway (e.g., by function, intended audience, or suggested timing within therapy) and can be used to filter what is displayed on the therapist’s pathway screen.
Once designed, the pathway can be saved as a draft or published and sent to the client. The client receives the notification of the new assignment either via email or the coaching app on their phone, tablet, or desktop.
A Take-Home Message
Success in therapy is heavily reliant on homework completion. The greater the compliance, the more likely the client is to have a better treatment outcome (Mausbach et al., 2010).
To improve the likelihood that clients engage with and complete the assignments provided, homework must be appropriate to their needs, have a sound rationale, and do the job intended (Beck, 2011).
Technology such as Quenza can make homework readily available on any device, anytime, from any location, and ensure it contains clear and concise psychoeducation and instructions for completion.
The therapist can easily create, copy, and tailor homework and, if necessary, combine multiple activities into single pathways. These are then shared with the click of a button. The client is immediately notified but can complete it at a time appropriate to them.
Quenza can also send automatic reminders about incomplete assignments to the client and highlight their status to the therapist. Not only that, but any resulting questions can be delivered securely to the therapist with no risk of getting lost in a busy email inbox.
Why not try the Quenza application? Try using some of the existing science-based activities or create your own. It offers an impressive array of functionality that will not only help you scale your business, but also ensure proactive, regular communication with your existing clients.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free.
- Beck, J. S. (2011). Cognitive behavior therapy: Basics and beyond. Guilford Press.
- Dweck, C. S. (2017). Mindset: The new psychology of success. Robinson.
- Mausbach, B. T., Moore, R., Roesch, S., Cardenas, V., & Patterson, T. L. (2010). The relationship between homework compliance and therapy outcomes: An updated meta-analysis. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 34(5), 429–438.
- Ribbers, A., & Waringa, A. (2015). E-coaching: Theory and practice for a new online approach to coaching. Routledge.
- Shapiro, S. L. (2020). Rewire your mind: Discover the science and practice of mindfulness. Aster.
- Tang, W., & Kreindler, D. (2017). Supporting homework compliance in cognitive behavioural therapy: Essential features of mobile apps. JMIR Mental Health, 4(2).
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (42)
- Coaching & Application (54)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (50)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (25)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (43)
- Optimism & Mindset (32)
- Positive CBT (25)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (45)
- Positive Emotions (30)
- Positive Leadership (14)
- Positive Psychology (32)
- Positive Workplace (33)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (41)
- Resilience & Coping (34)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (36)
- Software & Apps (13)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (44)
- Therapy Exercises (35)
- Types of Therapy (58)








