Goal-Setting: 20 Templates & Worksheets for Achieving Goals
 We all have goals, some big, some small, some safe, and some bold.
We all have goals, some big, some small, some safe, and some bold.
We wish to become a painter, to move to a new house, to write a book, to eat healthily, to exercise more, to become less anxious, and to run a marathon.
The list is endless, if ill defined. And yet, how much do we really want each one?
If something is vital to us, we need to make plans.
So, how do we do this?
Goal setting is widely accepted as the most effective way to focus our attention on the right activities, energize us, and increase our commitment (Sheard, 2013).
And yet, unless the goal is well formulated, the strategy appropriate, and the actions directed, it will lack purpose, relevance, direction, and accountability (Ogbeiwi, 2017).
Thankfully, this is an area that has received considerable scientific attention.
Goals are most effective when we use well-formulated frameworks that provide a logical, reliable platform to plan and monitor their completion.
Use the techniques and tools that follow to inspire you and find out what you want to achieve, why, and how you are going to do it.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free. These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques to create lasting behavior change.
This Article Contains:
- 3 Ways to Set Achievable Goals
- Our 5 Favorite Goal-Setting Worksheets
- What Are SMART Goals? A Template
- Goal-Setting Tools for Therapy and Coaching
- 2 Templates for CBT and DBT
- Worksheets for Teachers and Students
- Goal Planning With Children
- 2 Templates for Businesses and Employees
- Worksheets for Achieving Life Goals
- A Look at Daily and Weekly Goal Planners
- A Take-Home Message
- References
3 Ways to Set Achievable Goals
There are many types of goals. But ultimately, all goals boil down to one thing:
Change.
We need to move from one state to another, from where we are now to where we want to be.
Goal types
Firstly, what sort of goal do you want to achieve?
- Outcome goal – I want to be the best at X in the world.
- Performance goal — I want to better at X.
- Process goal — I want to train or practice at doing X.
- Delivery-focused goal — I want to deliver a change, such as a business, technology, or construction project.
The type of goal will influence your approach.
Discomfort zone
Goals should be meaningful. They should challenge us, change us, and sometimes lie in the discomfort zone.
In Your Best Year Ever, Michael Hyatt (2019) outlines four steps (modified below) for defining goals that stretch us and help us overcome our built-in resistance.
- Acknowledge the value of moving outside the comfort zone.
Accept that comfort may not lead to growth.
Recognize and acknowledge that there is value in discomfort. - Lean in.
Take the opportunity to challenge yourself.
This may require a change in mindset. - Recognize your fear.
Own the negative emotions that arise.
Decide if the rewards outweigh the fear. - Don’t overthink it.
Avoid ‘paralysis by analysis.’
Sometimes you take the next step even when the end goal remains unclear.
Meaningful goals
Humans have a set of innate psychological needs, one of which is to add meaning to life (Ryan & Deci, 2018).
Does this goal align with your overall life goals?
Use the steps below to focus on becoming more aware of the most meaningful things in your life (modified from Ivtzan, Chan, Gardner, & Prashar, 2011; Ivtzan, 2016):
- Sit comfortably, relax.
- Close your eyes.
- Become aware of your breathing.
- Inhale deeply and slowly.
- Concentrate on each breath; observe it.
- Visualize yourself in the future, living a full and meaningful life.
- Connect fully to the experience.
- Try not to dwell on how you got there.
- Shift attention to your body and feel the sensations that arise.
- Breathe into and explore these sensations; let them spread over your whole body.
- When you open your eyes, you should experience the full effect of the meditation.
As you refine your goals, make sure they continue to align with the picture you have created of a meaningful life.
Our 5 Favorite Goal-Setting Worksheets

The more vividly they are captured, the more likely you are to accomplish them.
GROW model
The GROW model (Goals, Reality, Options, and Way Forward) is a simple but highly effective method for setting goals, recognizing where you are now, and identifying what to do next (Whitmore, 2014).
Complete the four worksheets as follows:
Goal setting
- Establish where you want to be.
- Where do you want to get to, and how will you know when you arrive?
- Complete the Goal Setting Worksheet with your answers.
What is your current reality?
- Where are you right now with this goal?
- What are the issues and challenges?
- How far away are you from your goal?
- Complete the Reality Worksheet with your realistic insights.
What options do you have?
- What are the options for overcoming the obstacles in your way?
- How do you get to where you want to be?
- Complete the Options Worksheet with the options available to you.
What is the way forward?
- What will you do?
- Convert the options into actions.
- Complete the Way Forward Worksheet with your completed plan of action.
The Wheel of Success
What abilities do you have or need to deliver your goals?
The Wheel of Success identifies the skills and abilities that promote your very best performance (Whyte, 2015).
- Identify a list of performance attributes required to perform successfully.
- Assign a score (0–4) to each that truthfully represents where you are now.
- Assign another score (0–4) that identifies how good you believe you need to become.
For example, a runner training for a fast marathon time may have the speed but lack endurance.
| Attributes for marathoner | Current self rating | Future target score |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 4 | 4 |
| Endurance | 2 | 5 |
| Nutrition | 3 | 4 |
| Rest | 3 | 4 |
| Motivation | 4 | 5 |
By scoring where you are now (blue) and where you want to be (green), it is possible to focus time, energy, and resources, on improving areas where you fall short.
Improving your skills
How do you improve the skills you have identified?
Thankfully, we know the answer.
Research has confirmed that deliberate practice results in expertise.
- The task should be neither too easy nor too hard.
- Ongoing feedback is required to optimize performance.
- There must be an opportunity to repeat the task, correct errors, and improve.
The quality and the form the deliberate practice takes are more important than the number of hours devoted to performing the task (Ericsson, 2007; 2012).
What motivates you?
Identify and connect with the motivation behind each goal.
Intrinsic motivation – being driven by internal rewards – increases engagement and the likelihood that you will reach the goal (Ryan & Deci, 2018).
Michael Hyatt (2019) has the following suggestions:
- Connect with your why; identify your key motivations.
Why is this goal important?
Write down the reasons, prioritize, and connect with them. - Master your self-motivation; identify your reward.
Identify and anticipate the reward of completing the goal.
Recognize what is personal to you, rather than extrinsic rewards such as financial gain. - Build your team; identify who can help.
Your bonds with friends, family, and colleagues can help fuel success through learning, encouragement, accountability, and competition.
Goals that align with your values – personal growth, contributing to the broader community, etc. – are strong intrinsic motivators and increase vitality.
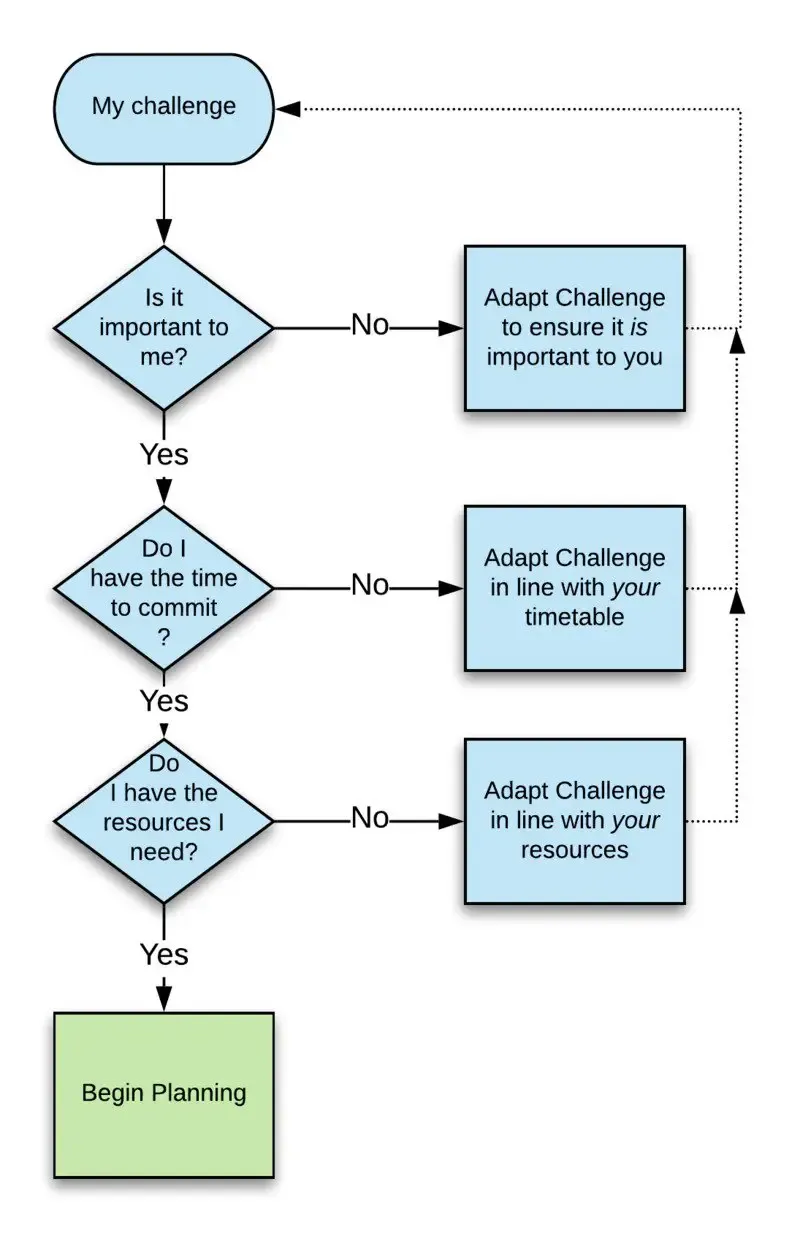
The flow of success
Are you ready to begin setting clear and defined SMART goals?
Follow the steps in the diagram below (adapted from Whyte, 2015):
If you answer ‘no’ to any of the questions, then you must revise the challenge or the environment before setting the goal.
Once you have answered ‘yes’ to all three questions, you are ready to define the goal to meet the challenge head on.
What Are SMART Goals? A Template
Goal setting not only helps you to complete the task, but also impacts wellbeing, represents your strive to achieve personal change, and enhances your meaning and purpose in life (Sheard, 2013).
To achieve something big, you need to break it down into a set of smaller, manageable tasks. Each time you complete one, you move nearer to the overall goal.
The widely used SMART, or slightly extended SMARTER, template ensures that each goal or sub-goal is realistic, achievable, and time-bound.
Specific – Goals should be clear and concise.
Measurable – What does success look like? How is it measured?
Achievable – The goal or task must be challenging but possible. Gently pushing the limits encourages improvement and growth.
Relevant – Does the goal fit with your overall life goals and core values?
Time-bound – When will you finish?
Exciting – What excites you? The benefits should be worthwhile to maintain commitment.
Reviewable – Circumstances change. Revisit the goals, and revise them if needed.
The SMART Goals Worksheet offers a valuable tool for defining and documenting a SMART goal.
Goal-Setting Tools for Therapy and Coaching

Goals should target the problem to be explored and outline the time available.
Setting new goals in therapy
What do you want to achieve? How do you want things to be different?
The following steps (modified from Wilding, 2015) help you set appropriate therapy goals:
- What is it you really want or wish for?
I wish I could find someone special in my life.
I wish I had a job that I was passionate about. - Spend time imagining what it would be like if it happened.
- Change the wording from ‘wish’ to ‘would like.’
I would like to find someone special in my life.
I would like a job that I was passionate about. - These statements feel different. ‘Would like’ is very positive; it suggests doing something about it, rather than sitting back and wishing.
Well done! You are well on the way to having a set of goals.
Prioritize your goals
Some goals are urgent but do not need analysis.
Acting upon them will immediately make your life better.
I would like to get the car fixed.
I would like to visit my mother; she is unwell.
Prioritize your goals and tackle the urgent ones first.
Act or think differently
Are the goals achieved through action or a change in the way you think?
Label your goals as either:
- Something that you need to do. (Action)
I’m not very confident in giving presentations – Work on it. - Something that you need to think about differently.
I’m not very tall – Learn to accept who you are. (Acceptance)
Labeling each goal will confirm whether you need to work on how you think, behave, or both.
2 Templates for CBT and DBT
Coaching needs to be goal driven to maximize its benefits.
The following two worksheets will help:
Coping Styles Formulation
If your coping strategies are not effective against the problems you face, then a set of actions are needed to direct the best way forward.
The Coping Styles Formulation worksheet identifies a list of problems, potential coping strategies, and the advantages and disadvantages of each one.
Mindfulness meditation
Mindfulness is often taught as part of Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT). Clients are helped to gain awareness of their thoughts and feelings and eliminate behaviors that interfere with goals (Soler et al., 2012).
Being in the right state of mind and grounding yourself in the present can help you identify and deliver your goals.
The 3-Step Mindfulness Worksheet is deceptively simple but provides a valuable way of practicing mindfulness throughout the day and bringing awareness to the present.
Worksheets for Teachers and Students
Goal setting is crucial to maximize and direct limited resources in education.
However, the teacher’s and student’s states of mind are equally important.
Motivation to learn
Like all of us, students and teachers need to be motivated to meet their goals.
This Self-Directed Speech Worksheet can help you change your self-directed speech and increase voluntary, or autonomous, motivation, which is linked to goal fulfillment (Ryan & Deci, 2018).
There are four steps to this exercise:
- Name the behavior you would like to change
- Name your inner voice
- List words that motivate you
- List sentences for when things get rough
Changing our inner narrative can be an effective way to motivate ourselves toward achieving personal, exciting goals.
Mindfulness in schools
Focus and attention are hugely important to the completion of goals. The absence of either will lead to an environment of distraction.
The Teaching Kids to Thrive worksheet discusses what mindfulness is and is not.
It helps to provide sufficient distance from disturbing or unwanted thoughts to act and deliver on outcomes.
Goal Planning with Children

Lack of focus, ease of distraction, and failing motivation are all possible challenges to overcome.
And yet, children asked to engage in a goal they value are likely to expend more effort and perform better (Koufoudakis, Erwin, Beighle, & Thornton, 2016).
Meaning and Valued Living
An excellent starting point for setting goals with children is to identify what inspires a sense of meaning in their lives.
Start by downloading and working through the three Meaning and Valued Living Exercises.
Self-awareness
Children need to gain an understanding of their strengths, along with what they find difficult.
The Self Awareness Worksheet is written for young children but is valuable at any age.
Through helping a child understand what they are good at, what they find hard, and what they like and don’t like, it is possible to define a set of goals that mix strengths and weaknesses.
Goals at any age should be challenging to encourage growth, but not beyond the child’s ability to complete, or they may become disillusioned and give up.
SMART for children
SMART goals are an effective way to direct focus in children.
The Student Goal Setting Worksheet is simple to complete, even for young children. Here is an overview of the questions and statements to consider:
- I am good at X.
- I am bad at X.
- What will I improve?
- How will I make these improvements?
- If my plan doesn’t work, what will I do?
Working through each of these will help a child understand which goals are important to them.
2 Templates for Businesses and Employees
Goal setting templates can be a useful base from which to start planning. We share two templates especially applicable to business and employees.
SMART goals for businesses
Many employees are comfortable with the idea of setting SMART goals.
However, despite the familiarity, their value within the work environment is often underestimated.
When taken seriously, SMART goals can motivate employees to succeed beyond their current level of expertise and identify future opportunities for training and development (Clough & Strycharczyk, 2015).
Visualization of your future
Focusing on positive mental images can prepare and protect our minds, help us cope with change, and increase self-belief.
Mentally working through each step in as much detail as possible—imagining sounds, smells, touch, thoughts, emotions, and physical responses—on our way to hitting goals can feel as real to the mind as actually performing the activity (Clough & Strycharczyk, 2015).
- Think of what you want to achieve.
- Imagine completing it successfully.
- How does it feel? How do you react?
- What do others look like?
- How do they react?
Imagine feeling confident, in control, and enjoying the challenge and the moment.
How to design your life (my process for achieving goals) – ModernHealthMonk
Worksheets for Achieving Life Goals
What are your dreams? What is important to you? What do you want to accomplish in life?
Document your life goals to provide the focus you need to make hopes and dreams real.
Martin Seligman’s PERMA model helps us to understand the elements of our lives that promote happiness.
Download the PERMA worksheet to understand your five core elements of wellbeing:
P – Positive emotions
E – Engagement
R – Relationships
M – Meaning
A – Accomplishments
A Look at Daily and Weekly Goal Planners

Review and change the goals over time, in line with your situation, your feelings, and what you want.
The Create a Legend Life Planner is available from Amazon and provides a high-quality home for your life goals.
The 90 Day Smart Goal Planner Calendar & Journal is also available from Amazon and uses SMART goals to target what you want to complete and change over the next three months.
A Take-Home Message
Imagine acting on the dreams that you keep tucked away, the ones that seem too big or too personal to share.
Make them real. Write them down as goals.
Let them inspire you and transform the world around you. Use goals to become the best possible you.
So, go ahead, take the resources from this article and identify significant goals that excite you. Break them down, define them as SMART goals, and turn them into something realistic and achievable.
By crafting them into something tangible and working through the individual actions, you will grow into the person you need to be to complete them.
Goal setting provides you with a means to navigate through a complex world and will encourage your long-term persistence.
Don’t let your goals remain a list of wishes.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free.
- Clough, P., & Strycharczyk, D. (2015). Developing mental toughness: Coaching strategies to improve performance, resilience, and wellbeing. Kogan Page.
- Ericsson, K. A. (2007). Deliberate practice and the modifiability of body and mind: Toward a science of the structure and acquisition of expert and elite performance. International Journal of Sport Psychology, 38(1), 4–34.
- Ericsson, K. A. (2012). Training history, deliberate practice, and elite sports performance: An analysis in response to Tucker and Collins review—What makes champions? British Journal of Sports Medicine, 47(9), 533–535.
- Hyatt, M (2019). Your best year ever. Embassy Books.
- Ivtzan, I., Chan, C. P. L., Gardner, H. E., & Prashar, K. (2011). Linking religion and spirituality with psychological well-being: Examining self-actualisation, meaning in life, and personal growth initiative. Journal of Religion and Health, 52(3), 915–929.
- Ivtzan, I. (2016). Second wave positive psychology: Embracing the dark side of life. Routledge.
- Koufoudakis, R., Erwin, H., Beighle, A., & Thornton, M. L. (2016). How feedback and goal-setting impact children’s recess physical activity. International Journal of Exercise Science, 9(4), 497–506.
- Neenan, M., & Palmer, S. (2001). Cognitive behavioural coaching. Stress News, 13, 15–18.
- Ogbeiwi, O. (2017). Why written objectives need to be really SMART. British Journal of Healthcare Management, 23(7), 324–336.
- Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2018). Self-determination theory: Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness. Guilford Press.
- Sheard, M. (2013). Mental toughness: The mindset behind sporting achievement. Routledge.
- Soler, J., Valdepérez, A., Feliu-Soler, A., Pascual, J. C., Portella, M. J., Martín-Blanco, A., … Pérez, V. (2012). Effects of the dialectical behavioral therapy-mindfulness module on attention in patients with borderline personality disorder. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 50(2), 150–157.
- Whitmore, J. (2014). Coaching for performance: growing human potential and purpose: The principles and practice of coaching and leadership. Nicholas Brealey Publishing.
- Whyte, G. P. (2015). Achieve the impossible: How to overcome challenges and gain success in life, work, and sport. Bantam Press.
- Wilding, C. (2015). Cognitive behavioural therapy: Techniques to improve your life. Hodder.
Let us know your thoughts
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (42)
- Coaching & Application (54)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (50)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (25)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (43)
- Optimism & Mindset (32)
- Positive CBT (25)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (45)
- Positive Emotions (30)
- Positive Leadership (14)
- Positive Psychology (32)
- Positive Workplace (33)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (41)
- Resilience & Coping (34)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (36)
- Software & Apps (13)
- Strengths & Virtues (30)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (44)
- Therapy Exercises (35)
- Types of Therapy (58)





What our readers think
This article is well-structured and science-based, with useful templates. Generous, helpful, practical and informative. Thank you Jeremy!
(Now I need to put it to use..)
Thank you this is exactly what I was looking for, today I started my journey on facing my obstacles head on and not creating diversions. Your templates will be valuable guides to help me acknowledge, get to the root of, work through and grow from the process of whatever I am seeking to improve. Just along writing this response was a start for me, thank you.
Do you receive some type of follow up?
Exactly what I was looking for in the first search!!! Dr. Sutton summarizes a HUGE amount of literature and proven techniques in one go. That is a huge time saver. I was looking for a template for doing weekly goal-setting as a family. We, as parents, have professional and personal goals and we want the children to begin thinking about goal setting for managing themselves, their schoolwork, sports, etc. This is a wonderful resource.
Thank you Dr. Sutton.
Thank you sir, Really its helped me.
Hi Roy,
So glad you found these templates helpful. Thanks for reading!
– Nicole | Community Manager